Anti-Inflammatory Diet to Reduce the Symptoms of LEMS
Written by |

Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome (LEMS) is a rare autoimmune disease characterized by progressive muscle weakness.
The disease is caused by the body’s own antibodies attacking nerve cells and damaging them.
Many treatments for LEMS are targeted at reducing inflammation, thereby slowing disease progression. An anti-inflammatory diet may also enhance the positive effects of anti-inflammatory medication.
What is an anti-inflammatory diet?
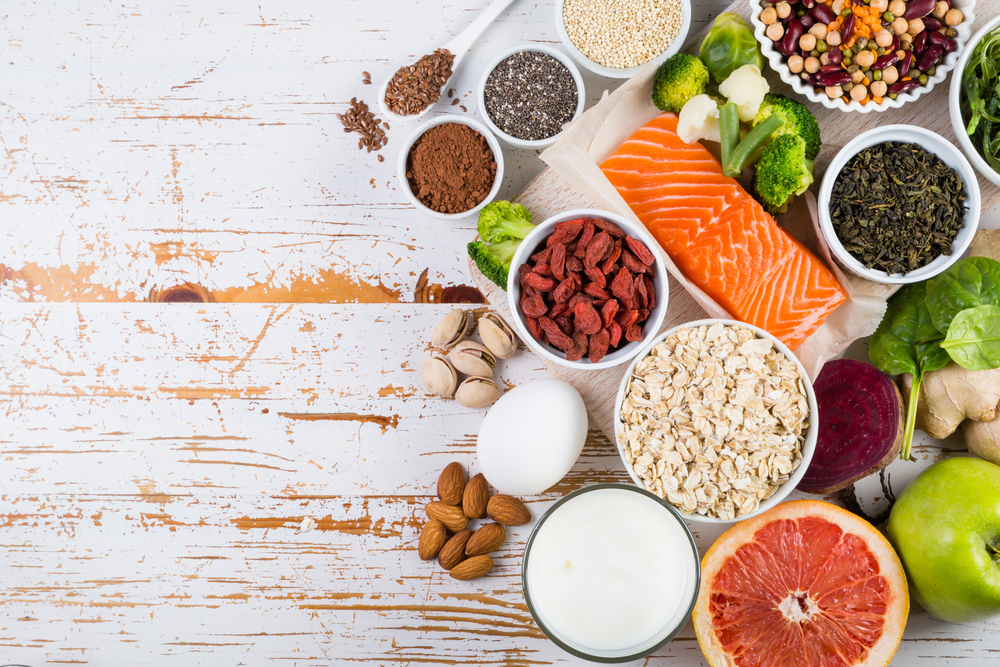
An anti-inflammatory diet is a diet that does not contain foods that are high in saturated fats, refined carbohydrates (white bread, sugary desserts, or soda), and red meat.
Foods that are good to eat in an anti-inflammatory diet include tomatoes, olive oil, green leafy vegetables, nuts (such as almonds and walnuts), fatty fish including salmon, tuna, and sardines, and fruits such as strawberries, blueberries, cherries, and oranges.
How can an anti-inflammatory diet help me?
It has been proposed that an anti-inflammatory diet may be able to help slow disease progression in autoimmune disorders. Clinical trials are underway to test this hypothesis in patients with multiple sclerosis (MS), for instance.
An anti-inflammatory diet may also be beneficial for people with LEMS and although several studies have been conducted, it is difficult to draw broad conclusions as to the benefits of diet for many reasons. For example, many studies have not included good controls and have relied on patient-reported information.
What has been shown, however, is that diets with inflammatory potential may be involved in the physiological processes associated with neurodegenerative diseases.
How should I start an anti-inflammatory diet?
Before making any big changes, it’s always a good idea to talk to your physician and a registered dietitian. They can help you figure out foods to include and avoid while making sure that you are getting the nutrition and vitamins that you need.
Last updated: Oct. 11, 2019
***
Lambert-Eaton News is strictly a news and information website about the disease. It does not provide medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. This content is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this website.